What should be done for a surge-absorbing circuit for DC-load Solid-state Relays?
Countermeasures against DC Switching Output Noise Surges
When an L load, such as a solenoid or electromagnetic valve is connected, connect a diode that prevents counter-electromotive force. If the counter-electromotive force exceeds the withstand voltage of the Solid-state Relay output element, it could result in damage to the Solid-state Relay output element.
As a countermeasure, insert the elements in Figure 1 in parallel with the load. (Refer to the following figure.)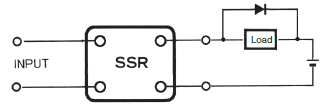
As an absorption element, the diode is the most effective at suppressing the counter-electromotive force. The release time for the solenoid or electromagnetic valve will, however, increase. Be sure to check the circuit before use. To shorten the time, connect a Zener diode and a regular diode in series. The release time will be shortened at the same rate that the Zener voltage (Vz) of the Zener diode is increased.
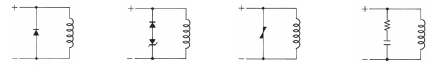
Figure 1: Absorption Element Example
| Absorption element |
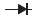 |
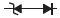 |
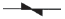 |
 |
| Diode | Diode + Zener diode | Varistor | CR | |
| Effectiveness | ○ | ○ | △ | × |
(Reference)
1. Selecting a Diode
Withstand voltage = VRM ≥ Power supply voltage × 2
Forward current = IF ≥ Load current
2. Selecting a Zener Diode
Zener voltage = VZ < (Solid-state Relay's connector − emitter voltage)* − (Power supply voltage + 2 V)
Zener surge reverse power = PRSM > VZ × Load current × Safety factor (2 to 3)
Note: When the Zener voltage is increased (VZ), the Zener diode capacity (PRSM) is also increased.