What relation is there between the contact spacing and the contact switching capacity?
If the contact spacing (contact gap) is large, the contact points can facilitate extinction of arc current which is generated when contact points open. Accordingly larger the contact spacing becomes, higher the current interrupting capacity of contact points becomes. Also, suppression of arc generation by accelerating the contact transfer rate can make the current interrupting capacity higher.
In general, as for the current of contact switching capacity, the influence of current interrupting capacity is greater than that of current carrying capacity, thus a high current interrupting capacity means a high current of contact switching capacity.
Additionally, as for the voltage of contact switching capacity, larger the contact spacing becomes, higher the voltage of contact switching capacity becomes.
Therefore, it is fair to say the contact spacing is basically proportional to the contact switching capacity.
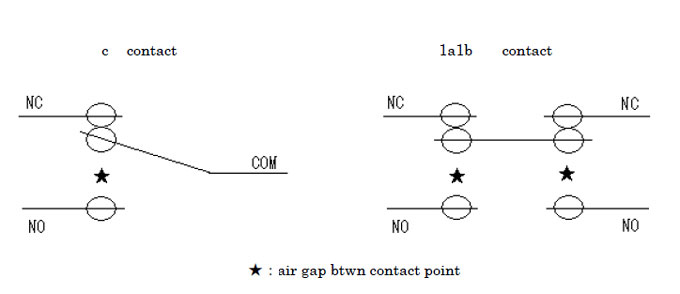
Furthermore, as for the types of contact structures, the contact point c structure including Micro Switches and Hinge Type Relay, and the contact point 1a1b structure including large Limit Switches and Plunger Relay are available. As shown in the following diagrams, the contact point c structure has a single contact gap, while the contact point 1a1b structure has two contact gaps. Thus, the latter has a higher current interrupting capacity and is more suitable for switching with a large-capacity load than the former.