What is "Two PID Control"?
Conventional PID control uses a single control block to control the responses of the Temperature Controller to a target value and to external disturbances. Therefore, the response to the target value will oscillate due to overshooting if importance is placed on responding to external disturbances with the P and I parameters set to small values and the D parameter set to a large value in the control block. On the other hand, the Temperature Controller will not be able to respond to external disturbances quickly if importance is placed on responding to the target value (i.e., the P and I parameters are set to large values). This makes it impossible to satisfy both the types of response in this case. Two PID control eliminates this drawback while maintaining the strengths of PID control. This makes it possible to improve both types of responses.
PID Control
1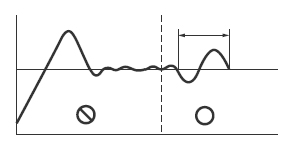
Response to the target value will be slow if response to the external disturbance is improved.
2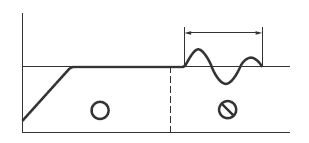
Response to the external disturbance will be slow if response to the target value is improved.
Two PID Control
3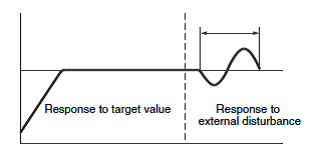 Controls both the target value and the external disturbance response.
Controls both the target value and the external disturbance response.