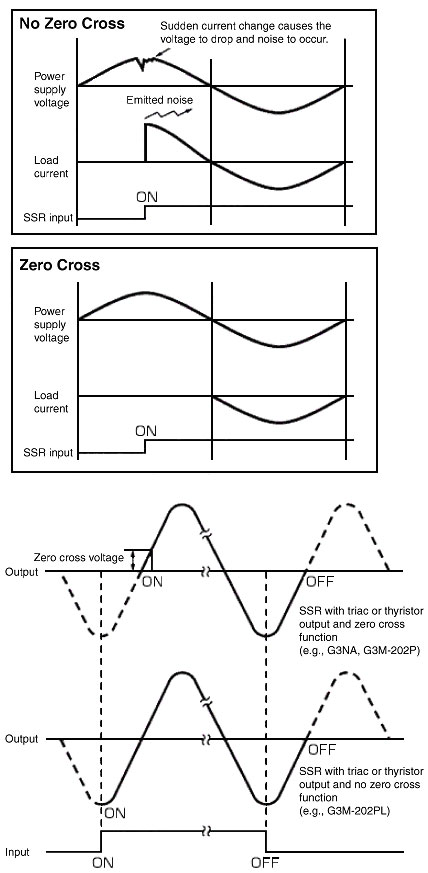
What is the zero cross function?
The zero cross function causes the Relay to turn ON when the AC load power supply approaches 0 V to suppress noise generated when the load current rises suddenly.
There are two types of noise: noise on power lines and noise emitted into open spaces. The zero cross function is effective against both types of noise.
A very large inrush current flows when lamps and similar equipment are turned ON, but the zero cross function causes the load current to always flow from a point near zero so that inrush current can be suppressed more compared to Solid-state Relays that do not have the zero cross function.
Ideally, the function turns ON near 0 V, but restrictions in the circuit configuration cause it to operate within the range of 0 V ±20 V. This voltage is called zero cross voltage.
https://www.ia.omron.com/support/faq/answer/include/faq02083/img/faq02083-1.jpg