What is the principle of operation of Long-distance Proximity Sensor the TL-L Series?
The circuit composition and the principle of operation are as follows.
1. Circuit composition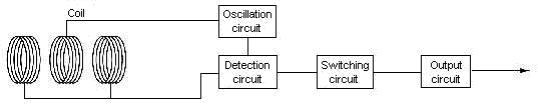
2. Principle of operation
It is called the differential coil type. It has the exciting coil that the high frequency oscillates and a couple of detector coil with which the differential is united, only the magnetic field by eddy current caused when metal approaches is detected.
Though the long distance can be detected, outline is large because there are a lot of coils.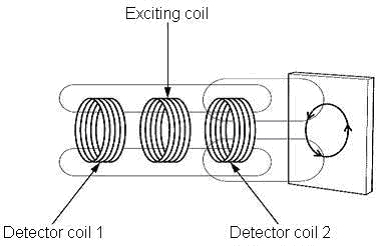
(1) 'Magnetic field by the exciting coil' is caused by the exciting coil at the center in a right and left detector coil.
(2) 'Eddy current magnetic field' is caused in a detector coil 2 by generating the eddy current on the surface of the sensing object when the sensing object approaches.
Detector coil 1:
Only 'Magnetic field by the exciting coil'
Detector coil 2:
Magnetic field by the exciting coil' and 'Eddy current magnetic field'
(3) The magnetic field of each detector coil is converted into the induction voltage.
Detector coil 1:
Only 'Induction voltage by the exciting coil'
Detector coil 2:
Induction voltage by the exciting coil' and 'Induction voltage by the eddy current magnetic field'
(4) It judges it from the value in which the voltage of detector coil 1 is subtracted from the voltage of detector coil 2 to judge the presence of the sensing object.
When there is a detection object:
Difference between coil 1 and coil 2= 'Induction voltage by the eddy current magnetic field'
When there is no detection object:
Difference between coil 1 and coil 2= none