What is the difference between an Solid-state Relay and a power MOS FET?
There are two main differences between Solid-state Relays and power MOS FETs.
Difference 1:
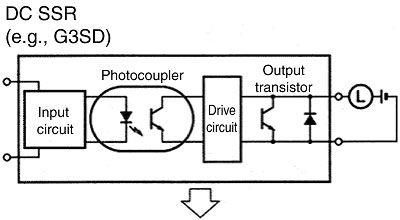
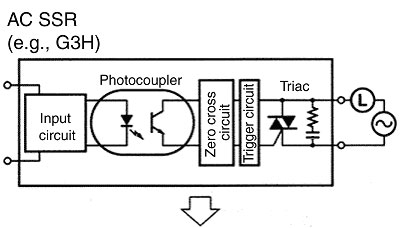
There are DC Solid-state Relays and AC Solid-state Relays.
A Power MOS FET Relay can be used with either a DC load or AC load.
Difference 2:
The leakage current is smaller compared with an Solid-state Relay.
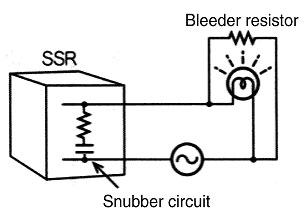
Solid-state Relay:
Leakage current causes the lamp to light dimly. A bleeder resistor is added to prevent this. The Solid-state Relay requires a snubber circuit to protect the output elements. This is the cause of Leakage current.
Power MOS FET Relays:
Because the leakage current is very small (e.g., 10 mA max.) the lamp does not light dimly. This is because a snubber circuit is not required to protect the output element MOS FET. A varistor is used to protect the MOS FET.
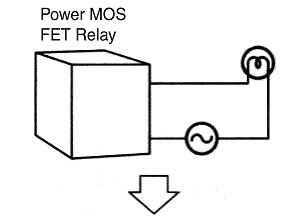 The circuit can be simplified and work reduced because a bleeder resistor is not required.
The circuit can be simplified and work reduced because a bleeder resistor is not required.