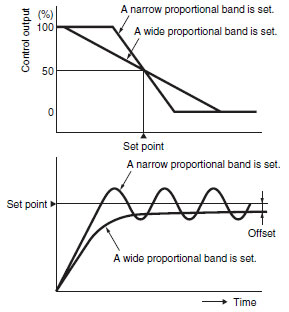
What is P Action?
With the P action, the control action produces an output of a size that is proportional to the input.
A proportional band is set for the set point. Controlling the manipulated variable (control output size) proportional to the deviation within the proportional band is call the proportional action.
Generally speaking, if the present temperature is lower than the proportional band, the manipulated variable is 100% and then it decreases in proportion to the deviation when the present temperature enters the proportional band. When the set point and present temperature are the same (i.e., then there is no deviation), the manipulated variable is 50%.
This enables smoother control with less hunting than ON/OFF operation.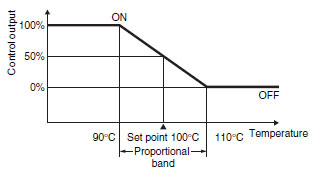
Example:
If a Controller with a temperature range of 0 to 400 °C is used with a 5% proportional band, the width of the proportional band will be 20 °C.
If the set point is 100 °C in this case, the output will remain ON until 90 °C is reached. When 90 °C is exceeded, the amount of time the output is OFF will increase until it is OFF for the same time it is ON (50%) at 100 °C.