What is "Output circuit"?
1. Open-collector Output
An output circuit where the emitter of the output circuit transistor is the common and the collector is open.
E6C2-CWZ6C (NPN open collector output)
E6C2-CWZ5B (PNP open collector output)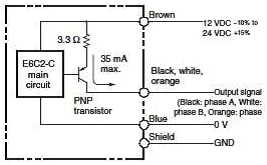
2. Voltage output
An output circuit where the emitter of the output circuit transistor is the common and a resistor is inserted between the collector and the power supply to convert the output from the collector to a voltage.
E6C2-CWZ3E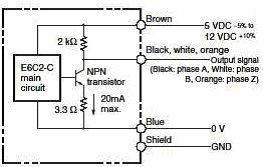
3. Line driver output
An output method that uses a special IC for high-speed, long-distance data transmission that complies with the RS-422A standard.
The signal is output as a differential secondary signal, and thus is strong with respect to noise.
A special IC called a line receiver is used to receive the signal output from a line driver.
E6C2-CWZ1X, E6C3-CWZ3XH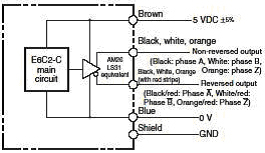
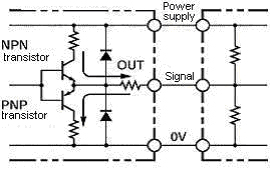
4. Complementary output
An output circuit with two output transistors (NPN and PNP) on the output.
These two output transistors alternately turn ON and OFF depending on the high or low output signal. When using them, pull up to the positive power supply voltage level or pull down to 0 V.
The complementary output allows flow-in or flow-out of the output current and thus the rising and falling speeds of signals are fast.
This allows a long cable distance.
They can be connected to open-collector input devices (NPN, PNP).
E6C3-CWZ5GH