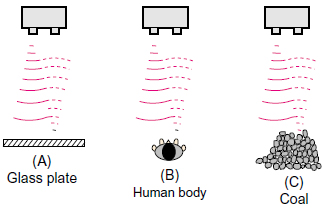
How does the reflection efficiency vary according to the type and the configuration of objects detected?
Types and configurations of sensing objects (Reflective Type)
Types and configurations of sensing objects are divided broadly into the following categories.
(A) Flat objects: liquid, box, plastic sheet, paper, glass, etc.
(B) Columnar objects: can, bottle, human body, etc.
(C) Granular or aggregated objects: ores, rock, coal, coke, plastic pellet, etc.
Reflection efficiency varies according to the configuration of these sensing objects.
In the case of (A), the largest amount of reflected waves is returned. However, it is greatly affected by the gradient of a sensing object.
In the case of (B) and (C), there is diffuse reflection and reflected waves are non-uniform. However, it is less affected by the gradient of a sensing object.